As part of the City's Pavement Asset Management Plan, several Capital Preventative Maintenance treatments will be employed that haven't been in regular use within the city for some time. These treatments are lower-cost treatments designed to be applied during the middle of a road's, thus improving pavement quality and helping slow further deterioration.
Micro-surfacing
A preservation treatment designed to fill small cracks, voids and correct other surface distresses in asphalt roadways. This treatment generally applies to streets that are in good structural condition, but are starting to show definite signs of aging. It restores the surface texture, seals the pavement and provides a new smooth and durable wearing surface for traffic.
Micro-surfacing consists of a cold applied mixture of liquid asphalt, fine aggregate, cement, water and other additives that are uniformly applied over the entire pavement surface and have fast set/cure times which allow for quick return of traffic (2-4 hours). Micro-surfacing is designed for use on higher volume major streets and lower volume local/residential streets. On major streets, it can be placed in either one or two courses, depending on the pavement condition, and has an overall thickness generally between 3/8 and 1/2 inch. On local streets, it is typically placed in one course at a uniform thickness of approximately 3/8 inches.
Micro-surfacing has low energy requirements, is environmentally safe, as it emits no pollutants, and is one of the most eco-efficient maintenance treatments available.
Cape Sealing
A preservation practice comprising of a two-step process that includes the application of a chip seal followed by a single course micro-surfacing treatment. This practice generally applies to streets that are in fair structural condition, and showing signs of aging that are more significant. It effectively repairs these types of pavements and provides a smooth and durable pavement surface.
Step 1 of the cape seal process involves placing a chip seal, which is an application of liquid asphalt sprayed over the pavement surface to penetrate the cracks and voids followed by a layer of aggregate (chips) applied with a spreader. The aggregate is compacted and embedded into the liquid asphalt using a rubber-tired roller. After the asphalt cures, the surface is swept to remove any loose stones, and the resulting thickness is approximately 3/8 to 1/2 inches with a rough texture. Step 2 involves the application of a micro-surfacing treatment over top of the chip seal to eliminate the rough surface texture and cover any loose aggregates. It is typically applied the day following the completion of the chip seal work.
Cape seals are also environmentally friendly as they too have low energy requirements, and emit no pollutants.
Step 1: Chip seal application
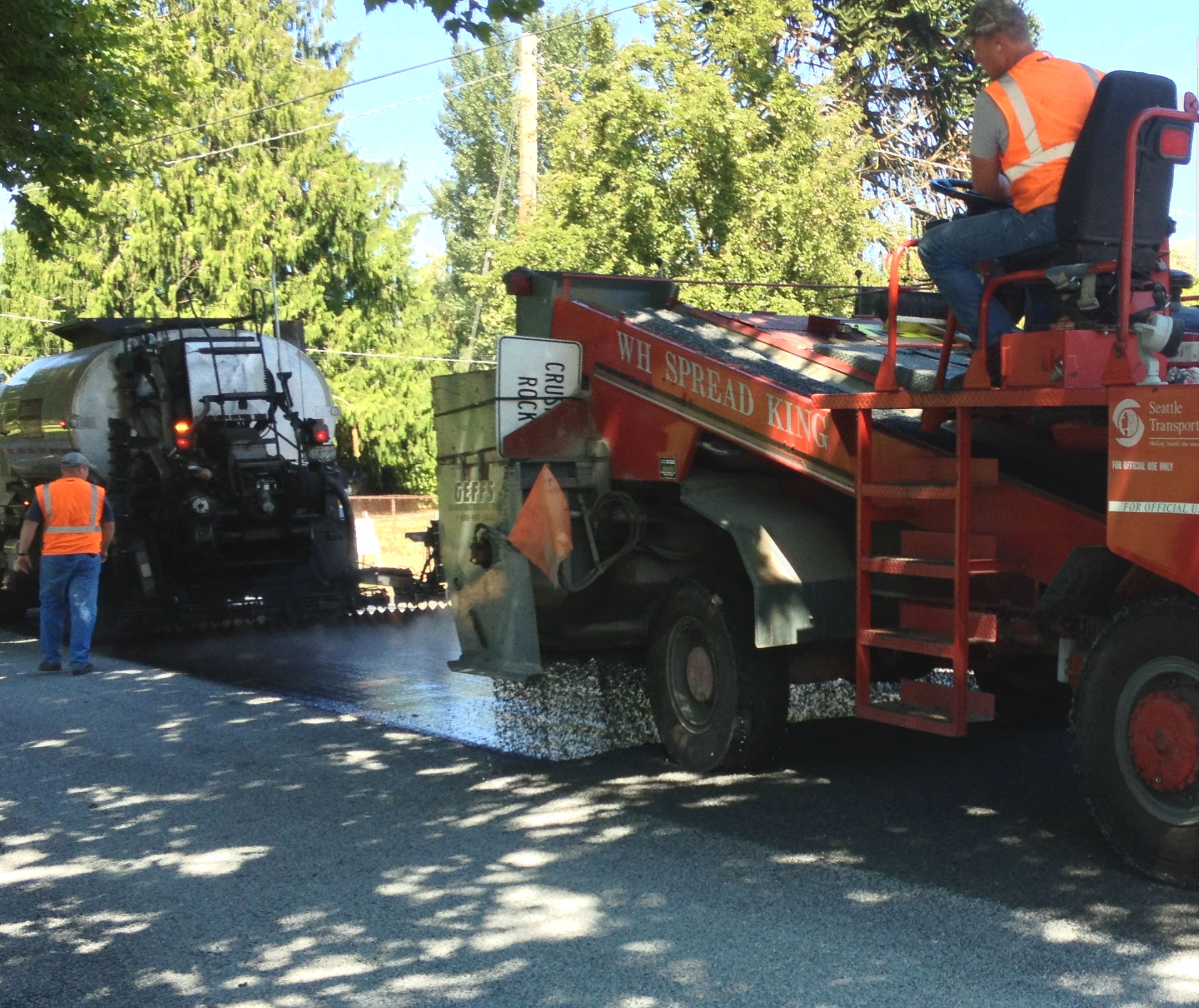

Step 2: Micro-surfacing application over chip seal